With the rapid advancement of information technology, the cost of Wi-Fi infrastructure and maintenance has become increasingly affordable. Wireless broadband networks are now widely adopted across various sectors such as business, tourism, residential areas, schools, and hospitals. More and more developed cities are integrating wireless networks into their urban infrastructure, considering it a key indicator of a city's operational efficiency, informatization level, and global competitiveness. The concept of a "Wireless Broadband City" not only offers citizens a fast and convenient way to access the internet, but also deeply integrates into daily life, enhancing public safety, emergency response, municipal management, e-education, and other essential services.
Located in the southern part of the Yangtze River Delta, Hangzhou is a core region within the coastal developed cities and the broader Yangtze River Delta economic zone. It serves as an interactive platform for citizens, businesses, educational institutions, healthcare providers, tourists, and government agencies, enabling seamless communication at any time and place. In line with the goals of the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan," Hangzhou's leadership accelerated the development of a wireless broadband metropolitan area network, adopting a forward-thinking and innovative approach to shape the city's future informatization. The project was planned in three phases. By the end of 2008, the first phase aimed to cover main roads and major scenic spots in the urban area, along with some office buildings and public spaces in parks, covering approximately 728 square kilometers. By the end of 2009, the coverage expanded to 16,600 square kilometers, achieving a comprehensive "wireless city" goal through point-to-line integration.
Once the first phase of the Hangzhou Wireless Broadband Metropolitan Area Network was completed, users could wirelessly connect laptops, portable TVs, and even mobile phones within the network coverage. In the future, government departments, organizations, and communities will be able to access multiple functions like news browsing, online information retrieval, public service updates, emergency alerts, video conferencing, and wireless voice communication via the internet. Additionally, public service initiatives such as road monitoring, traffic control, security surveillance, environmental data collection, and hydrological monitoring will also go "wireless." It can be said that the realization of a "wireless broadband city" lays a solid foundation for Hangzhou’s vision of becoming a "smart city."
Shanghai Ouhang Communication Technology Co., Ltd. actively participated in the bidding process for Hangzhou's Digital TV project and played a key role in designing and implementing the antenna feeder solution for the "Wireless Broadband City" initiative:
**Antenna Solution:**
Hangzhou Huasuo Digital TV Co., Ltd. focused on deploying 9,000 Wi-Fi access points in high-traffic areas and key development zones, including major government buildings, main roads, commercial districts, public squares, airports, train stations, hotels, office buildings, and universities. However, due to the need to integrate with existing infrastructure like streetlights, traffic lights, and surveillance poles, traditional corrugated coaxial cables and domestically produced layered cables faced several unresolved challenges.
(1) When cables are routed through poles, they tend to twist, causing copper skin to rupture or deform, which significantly impacts signal transmission.
(2) Some cables are not suitable for long-term outdoor use, with limited "three-proof" (UV-resistant, waterproof, anti-corrosion) protection, often lasting less than a year.
(3) The cables are too rigid, requiring a large turning radius, making installation difficult and inefficient.
(4) On-site cable assembly by different technicians leads to inconsistent installation quality, resulting in significant signal loss and standing wave issues.
(5) High signal loss and poor shielding performance further hinder effective communication.
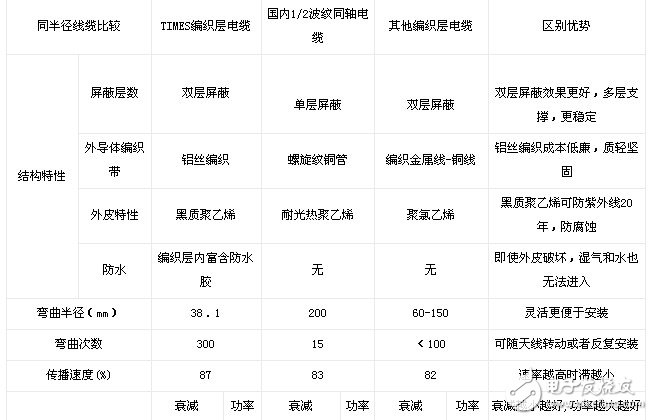
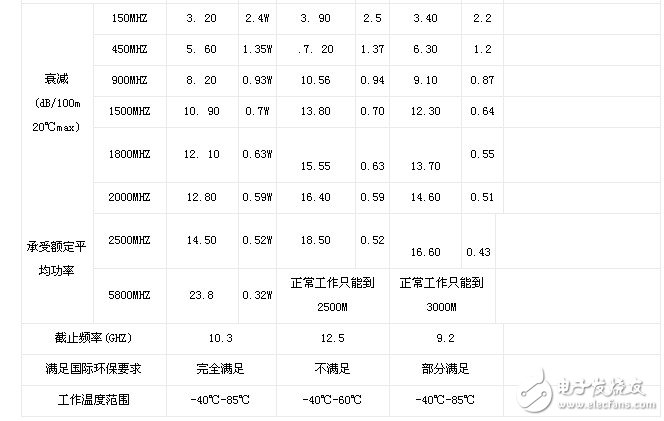
To address these challenges, Shanghai Ouhang Company provided tailored solutions after conducting technical support and on-site environmental analysis. They introduced the **TIMES LMR LW-600 DB** cable—flexible, lightweight, waterproof, and low-loss—along with matching connectors and high-precision tools.
For specific technical details, please refer to the following images:
air blown micro cable,air blown fiber optic cable,air blown fiber,air blown fiber cable
Guangzhou Jiqian Fiber Optic Cable Co.,ltd , https://www.jqopticcable.com