**Introduction to the Frequency of AC**
The frequency of alternating current (AC) refers to the number of complete cycles it completes in one second, measured in Hertz (Hz). It is inversely proportional to the period of the waveform. In everyday life, the standard frequency of AC power is typically 50 Hz, while in radio and communication technologies, frequencies can be much higher, often reaching kilohertz (kHz) or even megahertz (MHz).
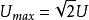 For example, the standard household voltage of 220V in many countries is an RMS value, with a peak voltage of approximately 311V.
**Modern Applications of AC**
In China, the standard AC frequency used in homes and industries is 50 Hz. Most electrical devices, such as lights and motors, operate on AC, which is commonly denoted by the symbol “~â€.
The behavior of AC changes over time, and its three main characteristics are the peak value, frequency (or period), and phase. Understanding these elements is essential when analyzing AC circuits. Unlike DC, AC involves components like capacitors and inductors, making the analysis more complex. However, the fundamental laws of electricity still apply.
According to Fourier’s theorem, any periodic function can be expressed as a sum of sine and cosine waves. This principle allows non-sinusoidal AC signals to be decomposed into multiple harmonic components.
**Frequency Cycle of Alternating Current**
Frequency measures how quickly the AC waveform changes over time. It is defined as the number of cycles per second and is represented by the symbol *f*, with units in Hertz (Hz). For instance, a 50 Hz AC signal completes 50 cycles every second. Higher frequencies may be measured in kilohertz (kHz) or megahertz (MHz).
For example, the standard household voltage of 220V in many countries is an RMS value, with a peak voltage of approximately 311V.
**Modern Applications of AC**
In China, the standard AC frequency used in homes and industries is 50 Hz. Most electrical devices, such as lights and motors, operate on AC, which is commonly denoted by the symbol “~â€.
The behavior of AC changes over time, and its three main characteristics are the peak value, frequency (or period), and phase. Understanding these elements is essential when analyzing AC circuits. Unlike DC, AC involves components like capacitors and inductors, making the analysis more complex. However, the fundamental laws of electricity still apply.
According to Fourier’s theorem, any periodic function can be expressed as a sum of sine and cosine waves. This principle allows non-sinusoidal AC signals to be decomposed into multiple harmonic components.
**Frequency Cycle of Alternating Current**
Frequency measures how quickly the AC waveform changes over time. It is defined as the number of cycles per second and is represented by the symbol *f*, with units in Hertz (Hz). For instance, a 50 Hz AC signal completes 50 cycles every second. Higher frequencies may be measured in kilohertz (kHz) or megahertz (MHz).
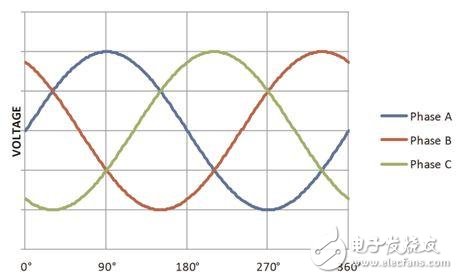
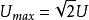 For example, the standard household voltage of 220V in many countries is an RMS value, with a peak voltage of approximately 311V.
**Modern Applications of AC**
In China, the standard AC frequency used in homes and industries is 50 Hz. Most electrical devices, such as lights and motors, operate on AC, which is commonly denoted by the symbol “~â€.
The behavior of AC changes over time, and its three main characteristics are the peak value, frequency (or period), and phase. Understanding these elements is essential when analyzing AC circuits. Unlike DC, AC involves components like capacitors and inductors, making the analysis more complex. However, the fundamental laws of electricity still apply.
According to Fourier’s theorem, any periodic function can be expressed as a sum of sine and cosine waves. This principle allows non-sinusoidal AC signals to be decomposed into multiple harmonic components.
**Frequency Cycle of Alternating Current**
Frequency measures how quickly the AC waveform changes over time. It is defined as the number of cycles per second and is represented by the symbol *f*, with units in Hertz (Hz). For instance, a 50 Hz AC signal completes 50 cycles every second. Higher frequencies may be measured in kilohertz (kHz) or megahertz (MHz).
For example, the standard household voltage of 220V in many countries is an RMS value, with a peak voltage of approximately 311V.
**Modern Applications of AC**
In China, the standard AC frequency used in homes and industries is 50 Hz. Most electrical devices, such as lights and motors, operate on AC, which is commonly denoted by the symbol “~â€.
The behavior of AC changes over time, and its three main characteristics are the peak value, frequency (or period), and phase. Understanding these elements is essential when analyzing AC circuits. Unlike DC, AC involves components like capacitors and inductors, making the analysis more complex. However, the fundamental laws of electricity still apply.
According to Fourier’s theorem, any periodic function can be expressed as a sum of sine and cosine waves. This principle allows non-sinusoidal AC signals to be decomposed into multiple harmonic components.
**Frequency Cycle of Alternating Current**
Frequency measures how quickly the AC waveform changes over time. It is defined as the number of cycles per second and is represented by the symbol *f*, with units in Hertz (Hz). For instance, a 50 Hz AC signal completes 50 cycles every second. Higher frequencies may be measured in kilohertz (kHz) or megahertz (MHz).

8KW-30KW MPPT Single-Phase Hybrid Inverter
8KW-30KW SIngle-Phase Hybrid Inverter(MPPT)
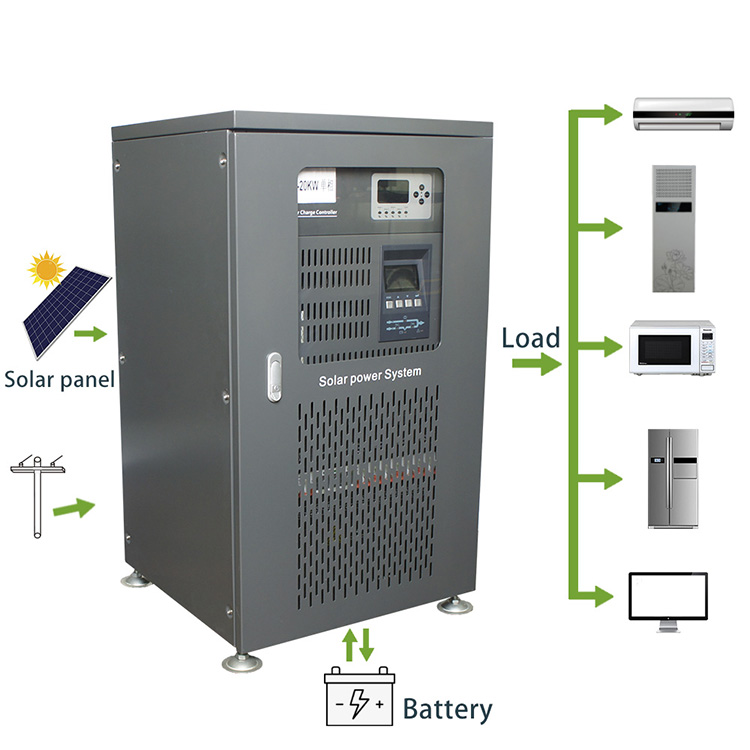

8KW-30KW MPPT Single-Phase Hybrid Inverter,Hybrid Solar Inverters, 48v Hybrid Solar Inverter
suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.xinlingvideo.com