Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) is an opportunistic infectious disease that typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems. It primarily causes damage to lung tissue and has become a major cause of mortality among high-risk groups, such as patients with diabetes, cancer undergoing chemotherapy, and those living with AIDS. The traditional treatments for PCP include sulfonamides and pentamidine, which are effective but often associated with significant side effects and rising drug resistance. In response to these challenges, some Chinese researchers have explored the use of traditional Chinese medicine, including Astragalus, Ginkgo, Garlic, and Artemisia annua L., in treating PCP. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Astragalus injection compared to standard treatments like compound sulfamethoxazole.
Ginkgolide
The study focused on comparing the efficacy of Astragalus injection with that of compound sulfamethoxazole in treating Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. The goal was to provide a scientific basis for clinical applications and explore alternative treatment options with fewer adverse effects.
1. Materials and Methods
1.1 Establishment of PCP Model: Forty clean-grade SD rats weighing between 180–220 g were used. Two rats were selected as the normal control group and received subcutaneous injections of physiological saline. The remaining rats were given dexamethasone sodium phosphate (1 mg/kg, twice weekly) to suppress their immune system. All rats had tetracycline hydrochloride added to their drinking water to prevent secondary infections. After 9 weeks, two rats from each group were euthanized, and lung tissues were examined using GMS staining to confirm the presence of Pneumocystis carinii cysts, indicating successful model establishment.
1.2 Drugs and Reagents: Ginkgolide (Sigma), Astragalus Injection (Chengdu Diao Jiuyi Pharmaceutical Factory), dexamethasone sodium phosphate (Tianjin Pharmaceutical Factory), tetracycline powder (Huabei Pharmaceutical Factory), and compound sulfamethoxazole tablets (Kunming Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.) were used. Astragalus injection was prepared by dissolving 40 mg of Ginkgolide in 0.8 mL of absolute ethanol and then mixing with 9.2 mL of Astragalus injection to create a solution.
1.3 Experimental Rats Grouping and Treatment: After model confirmation, 33 PCP rats were randomly divided into three groups. Group A served as the control without treatment. Group B received intraperitoneal injections of Astragalus solution (0.5 mL/rat, twice daily for 10 days). Group C was treated with a suspension of compound sulfamethoxazole via oral gavage (1 mL/day for 10 days). All rats were observed for one week post-treatment before being euthanized and their lungs analyzed.
1.4 Observation Indicators and Methods: Lung tissues were stained with GMS and examined under an oil microscope. The number of Pneumocystis cysts per 100 oil fields was counted. Additionally, HE staining was performed to assess pathological changes in lung tissue.
1.5 Statistical Analysis: Data were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 software to compare the average number of Pneumocystis cysts across the three groups.
2. Results
2.1 General Condition of the Disease: Before treatment, all groups showed signs of reduced appetite, dull fur, and breathing difficulties. After treatment, Groups B and C showed improvement in food intake, fur color, and breathing.
2.2 Changes in Body and Lung Weight: At the end of the experiment, body weight decreased in all groups, with the greatest loss in Group A. Lung weight and the lung-to-body weight ratio were highest in Group A, showing a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05).
2.3 Pneumocystis Infection and Cyst Count: Group A had a very high infection rate, while Groups B and C showed significant reductions in cyst counts after treatment (P < 0.01).
2.4 Pathological Findings: Group A exhibited moderate to severe interstitial pneumonia with alveolar thickening and inflammatory cell infiltration. Group B showed milder inflammation with fewer cysts and less exudate. Group C also showed mild inflammation but with more alveolar space than Group B.
3. Discussion
Currently, the most common method for establishing PCP models involves the use of glucocorticoids such as dexamethasone to suppress the immune system. This study successfully used this approach, confirming its reliability. Modern pharmacological research indicates that Astragalus has anti-inflammatory, immune-modulating, and anti-hypoxia properties. Combined with Ginkgolide, it showed promising results in reducing Pneumocystis infection in rat models. Although no significant toxicity was observed, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanism of action. Overall, the combination of Astragalus injection and Ginkgolide shows potential as a safe and effective treatment for PCP in clinical settings.
24 hours mechanical Timer
Instant indicator
Min.setting time:15 minutes. Max.setting timer:24 hours
With hand switch,can be switched to operating and
setting at any time
Instructions:
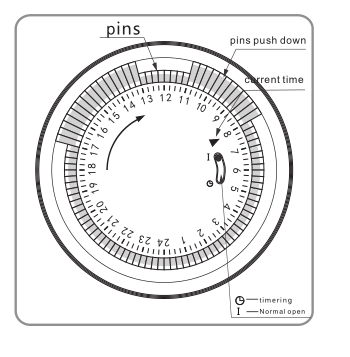
1. Set program: 1 pin is equivalent to 15 minutes. Determine desired start time and push down pins until desired
off time.
For instance, if you want electrical devices to work from 8:00am to 11:00am and from 13:00pm to 17:00pm, you
just need to put down allthe pins between the three period time.
2. Set the current time: Turning the dial clockwise until the arrow pointing to
current time.
For example,if now it is 8:00 am, please turn the dial and make sure the
arrow point to 8. (See the picture.)
3. Plug the electrical device directly into the timer. Make sure the electrical
device is power-on.
4. Plug the timer into electrical outlet and the electrical device will be work
according to the setting program.
Note: = Normal Ope n = Timing
Make sure the switch on the Timing position. If it
is on the [Normal Open" mode, the electrical device is
always power-on and the timer function no work.
Specifications:
|
Rated Voltage, Current and Power |
As shown on the label |
|
Time Setting Range |
15minutes24hours |
|
Working Temperature |
-10℃?+55℃ |
|
Operation |
Clockwise |
|
Insulation Resistance |
>100M |
|
Inherent Loss |
≤1W |
Application:
1. To enable high-power electric appliances to run automatically at off-peak time if there is different electricity
price according to different periods of time in some areas.
2. To use for electric appliances which need time control, such as water heaters, air conditioners, drinking
fountains, rice cookers, advertising lights and so on.
3. To control the charging time. For example, battery of electric bikes or mobile phones, storage batteries, etc.
4. Occasions which need switch on/off frequently, like interval spray irrigation for flowersand lawn, cyclical
adding oxygen to fish jar, fountains and so on.
5. Home safety precautions and lighting.
Caution:
1.D o not exceed the maximum ratings of the timer.
2.M ust reset the current time after power failure.
3.D o not plug the timer directly into the working electrical appliances.
4.U nless changing the setting, keep the program same every day.
5.D o not disassemble timer by yourself. Professionals service are needed for maintenance.
6.T his item is only for indoor use.
Mechanical Timer, mechanical timer socket, 24hr mechanical timer, mechanical timer plug, mechanical timer adaptor
NINGBO COWELL ELECTRONICS & TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD , https://www.cowellsocket.com